一、前言 1、SpringCache是Spring提供的一个缓存框架,在Spring3.1版本开始支持将缓存添加到现有的spring应用程序中,在4.1开始,缓存已支持JSR-107注释和更多自定义的选项。
2、Spring Cache利用了AOP,实现了基于注解的缓存功能,并且进行了合理的抽象,业务代码不用关心底层是使用了什么缓存框架,只需要简单地加一个注解,就能实现缓存功能了,做到了对代码侵入性做小。
3、由于市面上的缓存工具实在太多,SpringCache框架还提供了CacheManager接口 ,可以实现降低对各种缓存框架的耦合。它不是具体的缓存实现,它只提供一整套的接口和代码规范、配置、注解等,用于整合各种缓存方案,比如Caffeine、Guava Cache、Ehcache。
二、SpringCache深入 一、SpringCache大致原理
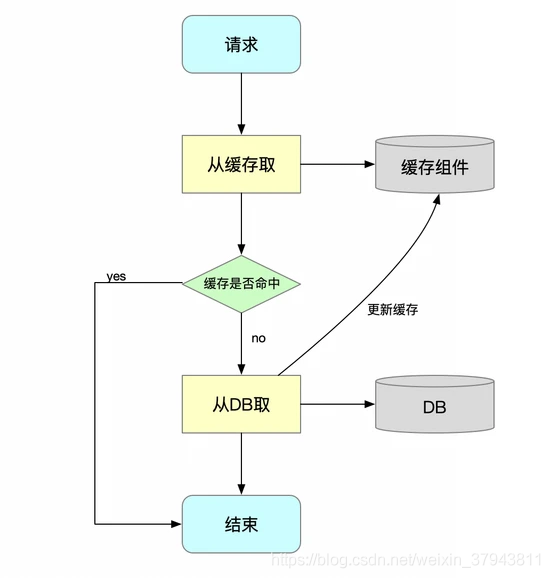
在SpringCache官网中,有一个缓存抽象的概念,其核心就是将缓存应用于Java方法中,从而减少基于缓存中可用信息的执行次数。换句话来说。就是每次调用目标方法前,SpringCache都会先检查该方法是否正对给定参数执行,如果已经执行过,就直接返回缓存的结果。(通俗的讲,就是查看缓存里面是否有对应的数据,如果有就返回缓存的数据),而无需执行实际方法、如果该方法上位执行。则执行该方法(缓存中没有对应的数据就执行方法获取对应数据,并进行缓存),并缓存结果并返回给用户。这样就不用多次去执行数据库操作,减少cpu和io的消耗。
二、SpringCache为我们提供了两个接口: 1、org.springframework.cache.Cache:
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合
2、org.springframework.cache.CacheManager:
CacheManager接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等;
三、SpringCache概念 1、Cache接口: 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有 如RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等
2、cacheResolver : 指定获取解析器
3、CacheManager : 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件;如:RedisCacheManager,使用redis作为缓存。指定缓存管理器
4、@Cacheable:在方法执行前查看是否有缓存对应的数据,如果有直接返回数据,如果没有调用方法获取数据返回,并缓存起来。
5、@CacheEvict: 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除。
6、@CachePut: 将方法的返回值放到缓存中
7、@EnableCaching: 开启缓存注解功能
8、@Caching: 组合多个缓存注解;
9、@CacheConfig: 统一配置@Cacheable中的value值
四、SpringCache注解中公共的属性 1、cacheNames :每个注解中都有自己的缓存名字。该名字的缓存与方法相关联,每次调用时,都会检查缓存以查看是否有对应cacheNames 名字的数据,避免重复调用方法。名字可以可以有多个,在这种情况下,在执行方法之前,如果至少命中一个缓存,则返回相关联的值。( Springcache提供两个参数来指定缓存名:value、cacheNames,二者选其一即可,每一个需要缓存的数据都需要指定要放到哪个名字的缓存,缓存的分区,按照业务类型分 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Cacheable(cacheNames = "tets") @Cacheable({"books", "isbns"}) public Book findBook (ISBN isbn) {...}
2 、KeyGenerator:key生成器
缓存的本质是key-value存储模式,每一次方法的调用都需要生成相应的Key, 才能操作缓存。
通常情况下,@Cacheable有一个属性key可以直接定义缓存key,开发者可以使用SpEL语言定义key值。若没有指定属性key,缓存抽象提供了 KeyGenerator来生成key ,具体源码如下,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class SimpleKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {public SimpleKeyGenerator () {public Object generate (Object target, Method method, Object... params) {return generateKey(params);public static Object generateKey (Object... params) {if (params.length == 0 ) {return SimpleKey.EMPTY;else {if (params.length == 1 ) {Object param = params[0 ];if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) {return param;return new SimpleKey (params);
由此可看出
如果没有参数,则直接返回SimpleKey.EMPTY ;
如果只有一个参数,则直接返回该参数;
若有多个参数,则返回包含多个参数的SimpleKey 对象。
当然Spring Cache也考虑到需要自定义Key生成方式,需要我们实现org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator 接口
默认的 key 生成器要求参数具有有效的 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法实现。
3、key:缓存的key,如果是redis,则相当于redis的key
可以为空,如果需要可以使用spel表达式进行表写。如果为空,则缺省默认使用key表达式生成器进行生成。默认的 key 生成器要求参数具有有效的 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法实现。key的生成器。key/keyGenerator二选一使用
4、condition:缓存的条件,对入参进行判断
可以为空,如果需要指定,需要使用SPEL表达式,返回true/false,只有返回true的时候才会对数据源进行缓存/清除缓存。在方法调用之前或之后都能进行判断。
condition=false时,不读取缓存,直接执行方法体,并返回结果,同时返回结果也不放入缓存。
condition=true时,读取缓存,有缓存则直接返回。无则执行方法体,同时返回结果放入缓存(如果配置了result,且要求不为空,则不会缓存结果)。
注意:
condition 属性使用的SpEL语言只有#root和获取参数类的SpEL表达式,不能使用返回结果的#result 。所以 condition = "#result != null" 会导致所有对象都不进入缓存 ,每次操作都要经过数据库。
五、Spel表达式 一、spel语法
具体语法可以参考此篇博客:SpEL表达式总结 - 简书
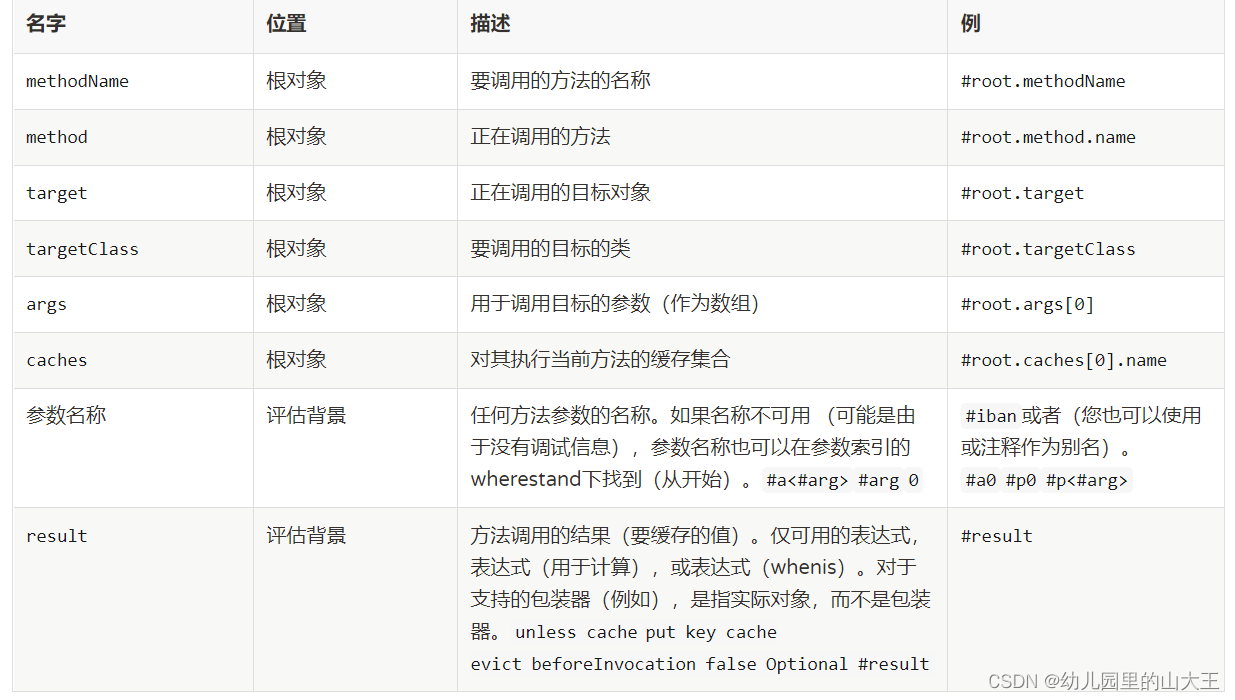
二、SpringCache也提供了root对象,具体功能使用如下。
三、使用spel表达式栗子
1、使用参数作为key:使用方法参数时我们可以直接使用“#参数名”或者“#p参数index”。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Cacheable(value="users", key="#id") public User find (Integer id) {@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0") public User find (Integer id) {@Cacheable(value="users", key="#user.id") public User find (User user) {@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0.id") public User find (User user) {
2、当我们要使用root对象的属性作为key时我们也可以将“#root”省略,因为Spring默认使用的就是root对象的属性。如:
1 2 3 4 @Cacheable(value={"users", "xxx"}, key="caches[1].name") public User find (User user) {
如果要调用类里面的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Cacheable(value={"TeacherAnalysis_public_chart"}, key="#root.target.getDictTableName() + '_' + #root.target.getFieldName()") public List<Map<String, Object>> getChartList (Map<String, Object> paramMap) {public String getDictTableName () {return "" ;public String getFieldName () {return "" ;
3、最好使用所有参数作为key,当然,也分情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Cacheable(cacheNames = "c2",key = "#id") public User getUserById (Long id,String username) {User user = new User ();return user;@Test void testGetUserById () {User u1 = userService.getUserById(98L , "dong" );User u2 = userService.getUserById(98L , "lisi" );
4、自定义key生成器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Component public class MyKeyGenerate implements KeyGenerator {@Override public Object generate (Object target, Method method, Object... params) {String s = target.toString()+":" +method.getName()+":" + Arrays.toString(params);return s;@Cacheable(cacheNames = "test",keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerate") public User getUserById (Long id,String username) {User user = new User ();return user;
五、各个注解详解 在四当中,已经把各个注解的公共属性抽了出来,这里只做一些注解的特有属性,当然,可能某些属性也是公有的。
一、@Cacheable: 在方法执行前查看是否有缓存对应的数据,如果有直接返回数据,如果没有调用方法获取数据返回,并缓存起来。
1、unless:条件符合则不缓存,是对出参进行判断
unless属性可以使用#result表达式。效果: 缓存如果有符合要求的缓存数据则直接返回,没有则去数据库查数据,查到了就返回并且存在缓存一份,没查到就不存缓存。
condition 不指定相当于 true,unless 不指定相当于 false
当 condition = false,一定不会缓存;
当 condition = true,且 unless = true,不缓存;
当 condition = true,且 unless = false,缓存;
2、sync:是否使用异步,默认是false.
在一个多线程的环境中,某些操作可能被相同的参数并发地调用,同一个 value 值可能被多次计算(或多次访问 db),这样就达不到缓存的目的。针对这些可能高并发的操作,我们可以使用 sync 参数来告诉底层的缓存提供者将缓存的入口锁住,这样就只能有一个线程计算操作的结果值,而其它线程需要等待。当值为true,相当于同步可以有效的避免缓存穿透的问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Cacheable(value="user_cache",key="#userId", unless="#result == null") public User getUserById (Long userId) {User user = userMapper.getUserById(userId);return user;
二、@CachePut:缓存更新
与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
他所具有的属性与@Cacheable相同就不多描述。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @CachePut(value = "user_cache", key="#user.id", unless = "#result != null") public User updateUser (User user) {return user;
三、@CacheEvict:清空缓存
注解的方法在调用时会从缓存中移除已存储的数据。
1 2 3 4 @CacheEvict(value = "user_cache", key = "#id") public void deleteUserById (Long id) {
1、allEntries:是否清空左右缓存。默认为false
当指定了allEntries为true时,Spring Cache将忽略指定的key
2、beforeInvocation:是否在方法执行前就清空,默认为 false
清除操作默认是在对应方法成功执行之后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回时也不会触发清除操作。使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定该属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素。
四、@Caching:可以让我们在一个方法或者类上同时指定多个Spring Cache相关的注解
1、 其拥有三个属性:cacheable、put和evict,分别用于指定@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Caching( cacheable = {@Cacheable(value = "stu",key = "#userName")}, put = {@CachePut(value = "stu", key = "#result.id"), @CachePut(value = "stu", key = "#result.age") } ) public Student getStuByStr (String userName) {StudentExample studentExample = new StudentExample ();return Optional.ofNullable(students).orElse(null ).get(0 );
五、@CacheConfig 抽取缓存的公共配置
我们每个缓存注解中 都指定 了value = “stu” / cacheNames=”stu” ,可以抽离出来,在整个类上添加
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = “stu”),之后每个方法中都默认使用 cacheNames = “stu”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 @CacheConfig(cacheNames = "stu") @Service public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {@Resource private StudentMapper studentMapper;@CachePut(key = "#result.id") @Override public Student updateStu (Student student) {return student;@Cacheable(key = "#id") @Override public Student getStu (Integer id) {Student student = studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);return student;@CacheEvict(allEntries = true, beforeInvocation = true) public void delSut (Integer id) {@Caching( cacheable = {@Cacheable(key = "#userName")}, put = {@CachePut(key = "#result.id"), @CachePut(key = "#result.age") } ) public Student getStuByStr (String userName) {StudentExample studentExample = new StudentExample ();return Optional.ofNullable(students).orElse(null ).get(0 );
三、SpringCache使用步骤: 一、Springboot整合redis与cache :
1、对于使用Springboot进行整合redis与cache,我们只需要引入
pom.xml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.redisson</groupId > <artifactId > redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 3.23.4</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > </dependencies >
application.properties 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 server.port =9001 spring.redis.host =192.168.55.101 spring.redis.port =6379 spring.redis.password =xxxx spring.cache.type =redis
RedissonConfig 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package com.cactus.springcache.config;import org.redisson.Redisson;import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;import org.redisson.config.Config;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import java.io.IOException;@Configuration public class RedissonConfig {@Value("${spring.redis.host:127.0.0.1}") private String redisIp;@Value("${spring.redis.port:6379}") private String redisPort;@Value("${spring.redis.password:password}") private String redisPassword;@Bean public RedissonClient redissonClient () throws IOException {Config config = new Config ();"redis://" + redisIp + ":" + redisPort);1 );return Redisson.create(config);
CacheConfig 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package com.cactus.springcache.config;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheProperties;import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;import java.time.Duration;@Configuration @EnableCaching public class CacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {@Bean public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration (CacheProperties cacheProperties) {RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();1 ));new StringRedisSerializer ()));new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer ()));Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null ) {if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null ) {if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {return config;
BaseResult 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 package com.cactus.springcache.common;import lombok.Data;@Data public class BaseResult {private int code;private String msg;private Object data;public static BaseResult success () {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();0 ;"success" ;return result;public static BaseResult success (String msg) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();0 ;return result;public static BaseResult success (Object data) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();0 ;"success" ;return result;public static BaseResult success (String msg,Object data) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();0 ;return result;public static BaseResult success (int code,String msg,Object data) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();return result;public static BaseResult error () {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();1 ;"error" ;return result;public static BaseResult error (String msg) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();1 ;return result;public static BaseResult error (Object data) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();1 ;"error" ;return result;public static BaseResult error (String msg,Object data) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();1 ;return result;public static BaseResult error (int code,String msg,Object data) {BaseResult result = new BaseResult ();return result;
User 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 package com.cactus.springcache.entity;import lombok.Data;@Data public class User {private String username;private String id;private Integer age;
TestController 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 package com.cactus.springcache.controller;import com.cactus.springcache.common.BaseResult;import com.cactus.springcache.entity.User;import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.UUID;@RestController @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestController {@RequestMapping("/user") @Cacheable(value = "cache_user",key = "'userTestCache'") public BaseResult testCache () {new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) {User user = new User ();"张三" + i +1 );18 +i);return BaseResult.success(list);@RequestMapping("/user/{id}") @Cacheable(value = "cache_user", key = "#id") public BaseResult testCache2 (@PathVariable("id") String id) {User user = new User ();"张三" );18 );return BaseResult.success(user);@CacheEvict(allEntries = true,cacheNames = "cache_user") @RequestMapping("/clean") public BaseResult clear () {return BaseResult.success();
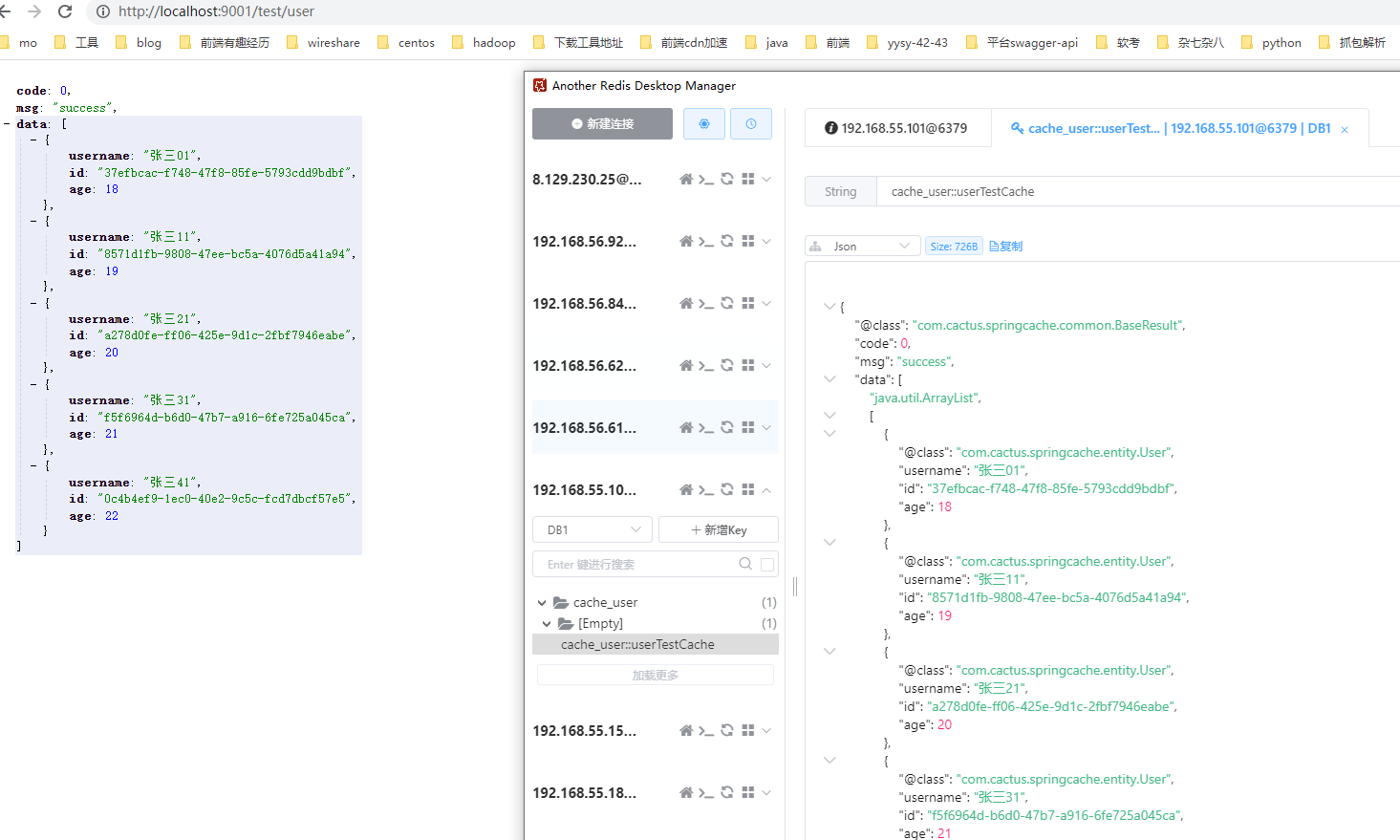
四、测试 1 GET http://localhost:9001/test/user
写入缓存
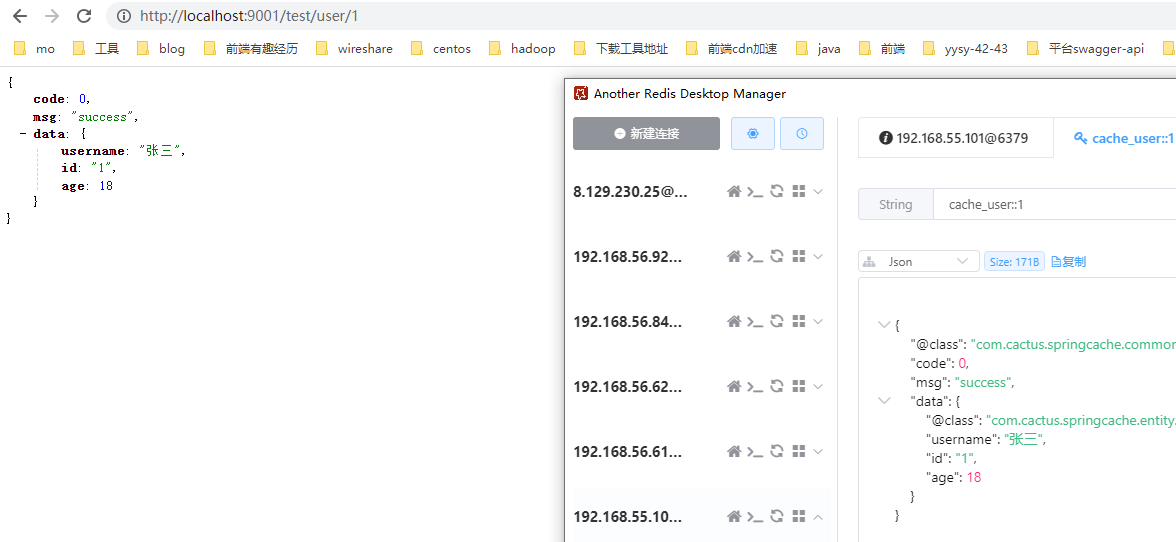
1 GET http://localhost:9001/test/user/1
单个写入
1 GET http://localhost:9001/test/clean
全部清除