Spring源码 Spring IOC初始化(暂时不看) 构造方法:this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
默认添加几个Processor:
internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
internalEventListenerProcessor
internalEventListenerFactory
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
获取到ConfigurationClassPostProcessor, 并调用postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) 方法
ConfigurationClassParser.doProcessConfigurationClass :扫描注解的地方
// Process any @Import annotations // processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors()
Spring自动配置加载
根据注解加载配置:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser
@EnableAutoConfiguration导入AutoConfigurationImportSelector:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector.getAutoConfigurationEntry
AutoConfigurationImportSelector 加载配置,先看Exclude注解有没有需要过滤的,在执行过滤器过滤出需要加载的autoConfiguration
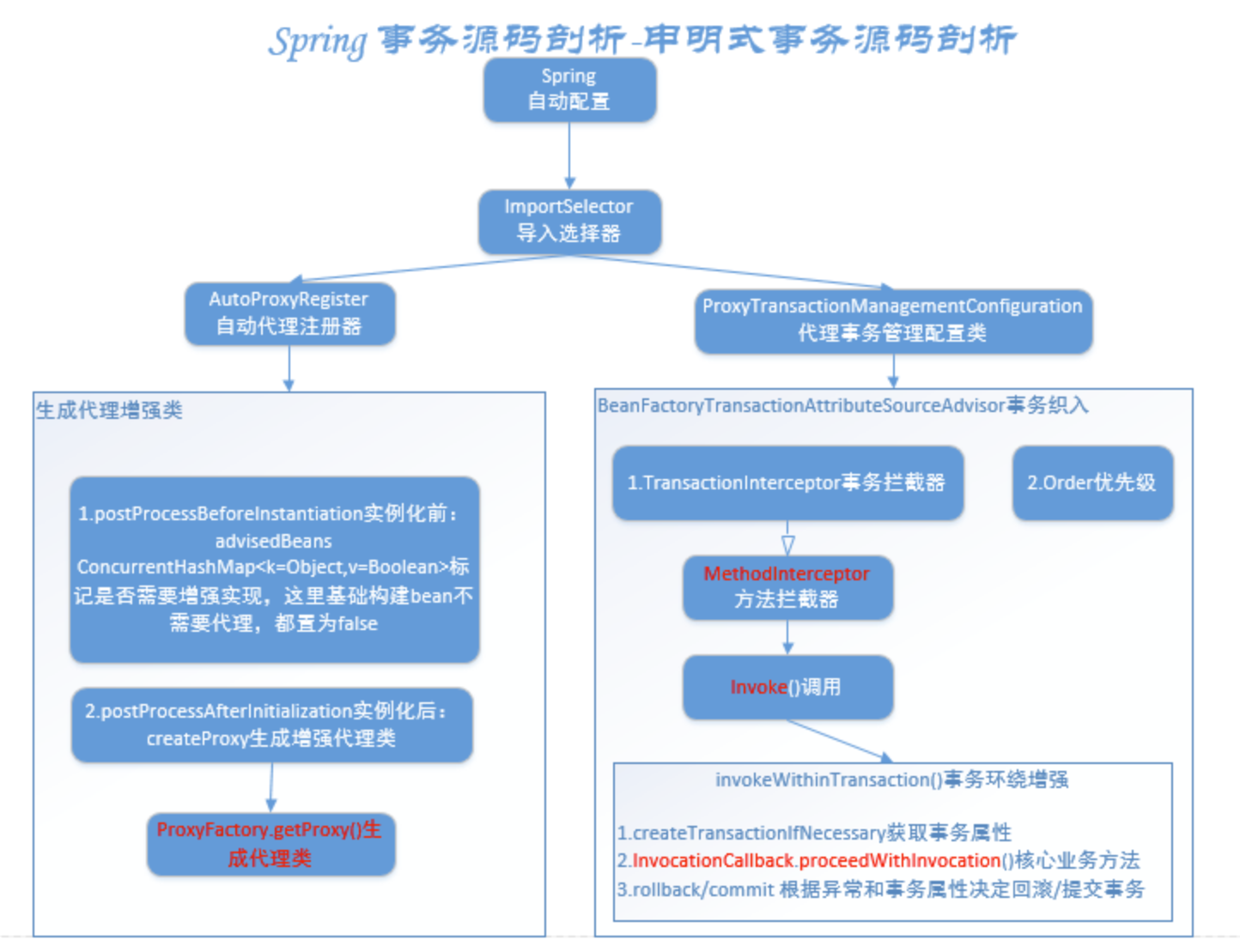
Spring transaction
Spring 框架中,事务管理相关最重要的 3 个接口如下:
PlatformTransactionManager: (平台)事务管理器,Spring 事务策略的核心。
TransactionDefinition: 事务定义信息(事务隔离级别、传播行为、超时、只读、回滚规则)。
TransactionStatus: 事务运行状态。
注解@EnableTransactionManagement 实现事务相关的Bean加载(现在自动配置使用AutoConfiguration实现)
TransactionInterceptor 主要的实现类,继承TransactionAspectSupport(定义了事务实现的方式)
实现原理为使用AOP+Threadlocal实现。
TransactionAspectSupport transactionInfoHolder:定义一个ThreadLocal,Spring采用ThreadLocal的方式,来保证单个线程中的数据库操作使用的是同一个数据库连接,同时,采用这种方式可以使业务层使用事务时不需要感知并管理connection对象,通过传播级别,巧妙地管理多个事务配置之间的切换,挂起和恢复。
@Transaction方法调用链条:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 WithinTransaction(Method method , @Nullable Class<?> targetClass , TransactionAspectSupport.InvocationCallback invocation ) throws Throwable {TransactionAttributeSource() ;TransactionAttribute(method , targetClass ) : null;TransactionManager(txAttr ) ;TransactionIfNecessary(ptm , txAttr , joinpointIdentification ) ;try {WithInvocation() ;TransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo , ex ) ;TransactionInfo(txInfo ) ;if (vavrPresent && TransactionAspectSupport .VavrDelegate .VavrTry(retVal ) ) {TransactionStatus() ;if (status != null && txAttr != null) {TransactionAspectSupport .VavrDelegate .TryFailure(retVal , txAttr , status ) ;TransactionAfterReturning(txInfo ) ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 protected TransactionAspectSupport.TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary (@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm, @Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {if (txAttr != null && ((TransactionAttribute)txAttr).getName() == null ) {new DelegatingTransactionAttribute ((TransactionAttribute)txAttr) {public String getName () {return joinpointIdentification;TransactionStatus status = null ;if (txAttr != null ) {if (tm != null ) {else if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this .logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification + "] because no transaction manager has been configured" );return this .prepareTransactionInfo(tm, (TransactionAttribute)txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);public final TransactionStatus getTransaction (@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {TransactionDefinition def = definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults();Object transaction = this .doGetTransaction();protected Object doGetTransaction () {DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionManager .DataSourceTransactionObject();this .isNestedTransactionAllowed());ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(this .obtainDataSource());false );return txObject;
Spring 事务处理 中,可以通过设计一个 TransactionProxyFactoryBean 来使用 AOP 功能,通过这个 TransactionProxyFactoryBean 可以生成 Proxy 代理对象
事务隔离实现 spring 事务隔离主要通过DataSourceTransactionManager 在开启事务的时候,设置对应的隔离级别到数据库连接中。
本质上事务的实现是通过设置数据库连接的隔离级别。即类似于 mysql> set global transaction_isolation ='read-committed'; 因此数据库的实现依赖于数据库支持的隔离级别
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Overridedo Begin(Object transaction , TransactionDefinition definition ) {try {if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() || txObject.getConnectionHolder() .isSynchronizedWithTransaction() ) {DataSource() .getConnection() ;if (logger.isDebugEnabled() ) {"Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction" );ConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon ) , true );ConnectionHolder() .setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true ) ;ConnectionHolder() .getConnection() ;DataSourceUtils .ConnectionForTransaction(con , definition ) ;PreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel ) ; ... }
@Transactional失效场景
注解导致的事务失效:
@Transactional 注解属性 propagation 设置错误,设置了以非事务的状态运行
@Transactional 注解属性 rollbackFor 设置错误,实际抛出的错误跟设置不一致
方法修饰符导致的事务失效
@Transactional 应用在非 public 修饰的方法上,在事务方法拦截执行中,非public方法不执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Nullable computeTransactionAttribute (Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {if (allowPublicMethodsOnly () && !Modifier.isPublic (method.getModifiers ())) {return null ;
在动态代理层面,若为也需要代理的方法为public才能正常代理。如JDK动态代理,通过接口代理,接口方法默认都是public。而Cglib基于类的代理中会默认判断是否为public方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method , Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { ... TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource() ;try { ... if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier .Public(method .getModifiers () )) {[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils .ArgumentsIfNecessary(method , args ) ;
同一个类中方法调用,导致@Transactional失效,在当前的bean中非事务方法调用事务方法为什么不生效?
当进行方法拦截的时候,方法拦截器首先获取当前动态代理的对象所代理的原始对象。如果判断当前的方法比如save方法没有Advice(增强),则直接调用原对象的方法,即这个时候调用的是FirstApp.save方法。
异常被 catch 导致@Transactional失效
数据库引擎不支持事务
相关文章 Spring事务原理完全解析
Spring AOP HandlerAdapter与InvocableHandlerMethod 对于Controller的方法,请求发送的时候通过HandlerAdapter调用InvocableHandlerMethod.doInvoke方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 protected Object do Invoke(Object... args ) throws Exception {ReflectionUtils .Accessible(getBridgedMethod () );try {BridgedMethod() .invoke(getBean() , args); ...
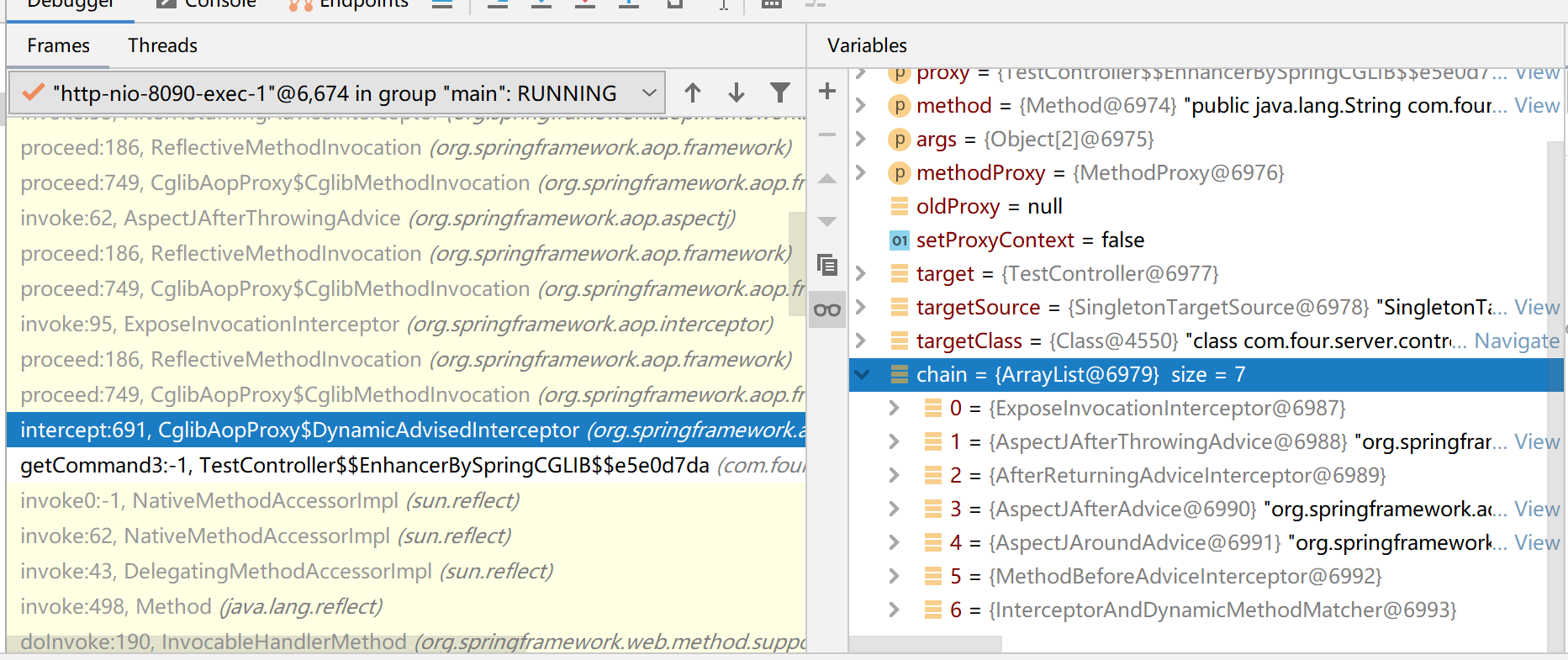
整体的调用流程
对于web的调用,首先通过InvocationHandlerMethod,设置方法可见,强制调用方法。
调用方法后,判断方法是否使用代理,若没使用代理,直接调用方法。若使用了代理,进入代理方法的invoke方法。
区分JDK代理、Cglib代理,获取Advisor的对应拦截链,分别进入到拦截类的proceed()方法执行中。
判断使用JDK代理还是Cglib代理
对于实际的Method调用,如果是代理对象的调用会分别进入各自的代理的invoke方法中,主要分为Cglib(CglibAopProxy)和JDK代理(JdkDynamicAopProxy)
DefaultAopProxyFactory:如何判断使用JDK代理还是Cglib代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public AopProxy createAopProxy (AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {if (config.isOptimize () || config.isProxyTargetClass () || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces (config)) {getTargetClass ();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException ("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation." );if (targetClass.isInterface () || Proxy.isProxyClass (targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy (config);return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy (config);else {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy (config);
CglibAopProxy的代理方法 CglibAopProxy 代理方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method , Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {false ;TargetSource() ;try {if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {AopContext .CurrentProxy(proxy ) ;true ;Target() ;Class() : null);InterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method , targetClass ) ;if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier .Public(method .getModifiers () )) {[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils .ArgumentsIfNecessary(method , args ) ;else {new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy , target , method , args , targetClass , chain , methodProxy ) .proceed() ;ReturnType(proxy , target , method , retVal ) ;
JdkDynamicAopProxy的代理方法 JdkDynamicAopProxy: 基于JDK的代理可以看出,对于基本的方法hashcode以及equals方法都是没有进行拦截的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method , Object[] args) throws Throwable {false ;try {if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils .EqualsMethod(method ) ) {[0 ] );else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils .HashCodeMethod(method ) ) {Code() ;else if (method .getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy .class ) {AopProxyUtils .TargetClass(this .advised ) ;else if (!this.advised.opaque && method .getDeclaringClass() .isInterface() && method .getDeclaringClass() .isAssignableFrom(Advised.class ) ) {AopUtils .JoinpointUsingReflection(this .advised , method , args ) ;if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {AopContext .CurrentProxy(proxy ) ;true ;Target() ;Class() : null);InterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method , targetClass ) ;if (chain.isEmpty() ) {[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils .ArgumentsIfNecessary(method , args ) ;AopUtils .JoinpointUsingReflection(target , method , argsToUse ) ;else {new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy , target , method , args , targetClass , chain ) ;() ;
AspectJ的方法织入 AspectJ的Aop 在方法调用的时候添加了AOP对应的拦截方法,根据对应的拦截类型